Exp 8Puzzle A* Academic IA Project (2016)
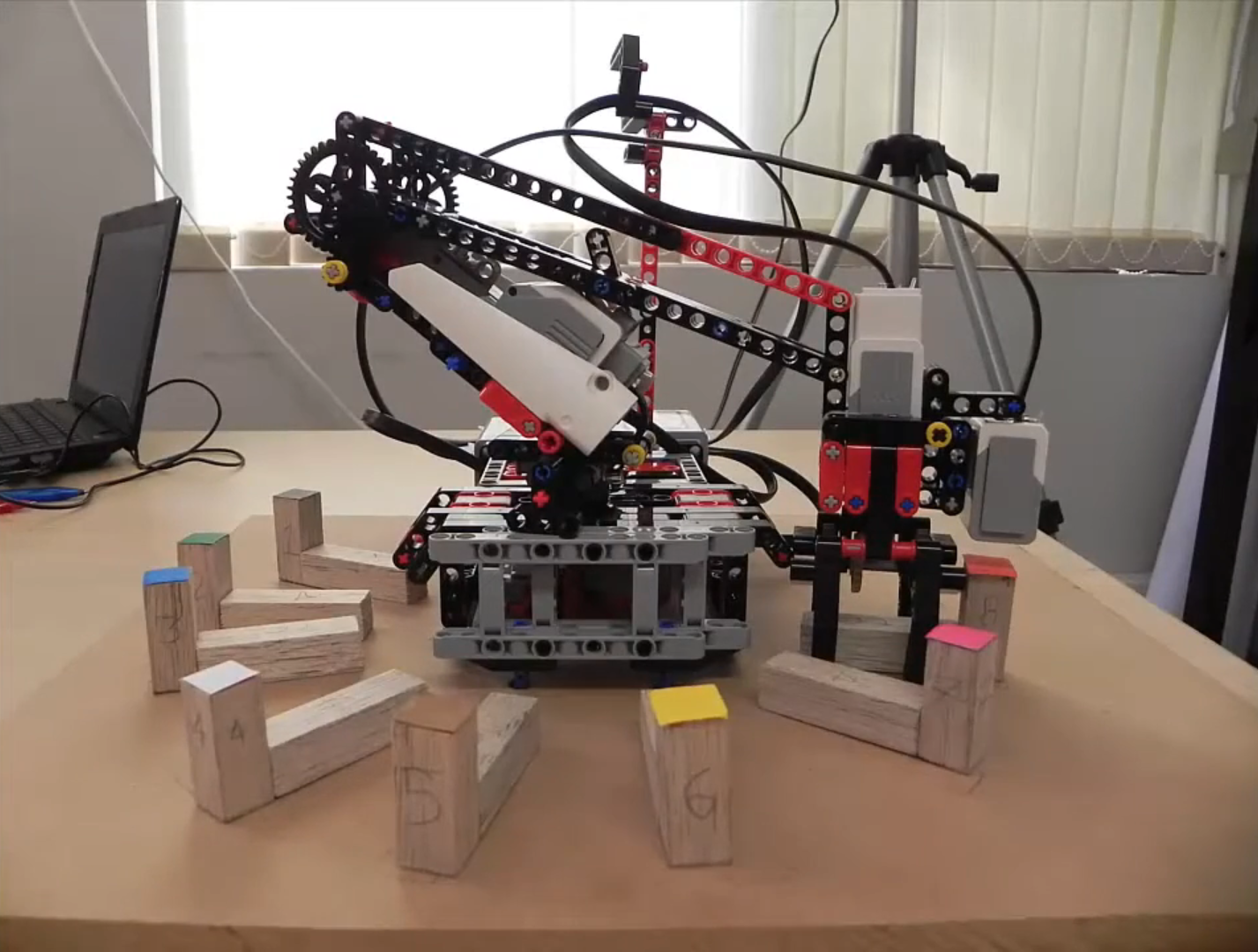
 In semester five (at 2016), I took an Artificial Intelligence course where I learned the basics about agents, multi-agent systems, heuristics, and others AI algorithms. At the end of the course, we were required to complete a project. In this case, the university had recently acquired 10 kits of the Lego EV3 Home Edition, and the instructor wanted the students to implement a “physical” project, such as a robot that uses an IA algorithm (learned from course) to solve a problem.
In semester five (at 2016), I took an Artificial Intelligence course where I learned the basics about agents, multi-agent systems, heuristics, and others AI algorithms. At the end of the course, we were required to complete a project. In this case, the university had recently acquired 10 kits of the Lego EV3 Home Edition, and the instructor wanted the students to implement a “physical” project, such as a robot that uses an IA algorithm (learned from course) to solve a problem.
I was responsible for the main software implementation and Lejos configuration (embedded OS to execute Java on the Brick). I completed this project with:
- Jorge Mario: Who was responsible for making optimizations to the software implementation.
- Felipe Gutierrez: Who was in charge of the structure and building of the robot.
- Miguel Angel: Who was tasked with research and creating documentation.
Skills/Tools
- Java
- Eclipse
- Basics of IA
- Robotics
8-Puzzle
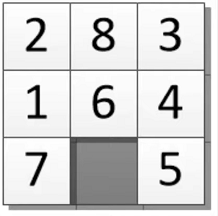 In the 8-puzzle problem, you have a 3x3 grid with tiles numbered 1 through 8 and one empty space. The goal is to move the tiles around until they are in order, resembling [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. In the AI course, this was suggested as a potential project to implement the A* algorithm with the Manhattan Distance heuristic.
In the 8-puzzle problem, you have a 3x3 grid with tiles numbered 1 through 8 and one empty space. The goal is to move the tiles around until they are in order, resembling [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8]. In the AI course, this was suggested as a potential project to implement the A* algorithm with the Manhattan Distance heuristic.
Project Algorithm A*
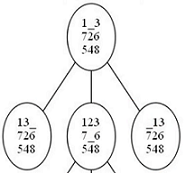
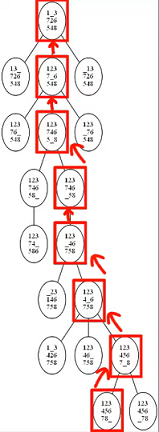 A* is an informed search algorithm that finds the shortest path between a given start node and a goal node in a weighted graph. A* employs a best-first search and applies a heuristic to estimate the cost of the cheapest path. The algorithm maintains a tree of paths originating at the start node and extends those paths one edge at a time until its termination condition is met.
A* is an informed search algorithm that finds the shortest path between a given start node and a goal node in a weighted graph. A* employs a best-first search and applies a heuristic to estimate the cost of the cheapest path. The algorithm maintains a tree of paths originating at the start node and extends those paths one edge at a time until its termination condition is met.
This algorithm has multiple applications, especially when the search has limited resources, such as in systems with agents where each agent has limited resources like mini robots, or is restricted as in NPCs controlled by a server. In another case, it may not be possible to analyze the entire environment because it is too vast to process and results in dense complexity, as seen in network routing and route planning.
Heuristic
A* uses a heuristic function, h(n), to estimate the cost of reaching the goal from node n. The function g(n) represents the exact cost of the path from the start node to n. A* combines g(n) and h(n) into f(n) = g(n) + h(n), which estimates the total cost of the cheapest solution through n.
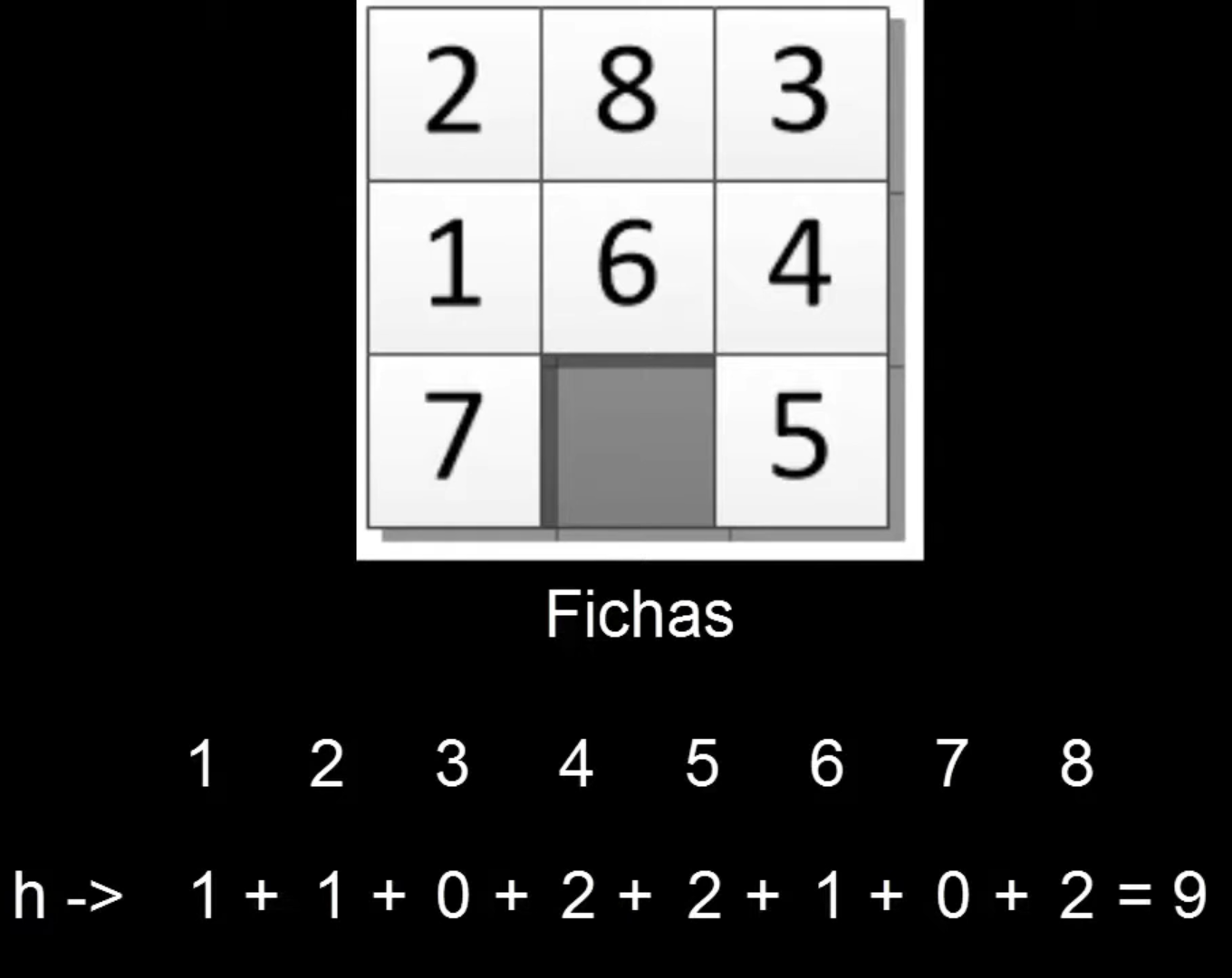
Manhattan Distance
In the context of the 8-puzzle problem, Manhattan Distance serves as a heuristic for the A* algorithm. It calculates the total number of moves required to move each block from its current position to the target position, allowing only horizontal or vertical moves. For each tile, the distance is the sum of the absolute values of the differences in the tile’s x and y coordinates between its current position and the goal position.
Here’s the formula for the Manhattan distance for a tile at position (x1, y1) and its goal position (x2, y2):
Manhattan Distance = |x1 - x2| + |y1 - y2|
What is LEGO EV3 Mindstorms?

https://www.lego.com/themes/mindstorms/downloads
LEGO Mindstorms is a kit consisting of various LEGO pieces that enable users to create programmable robots capable of interacting with the physical world. The kits include a range of LEGO elements, a programmable “Smart Brick,” motors, and sensors. The LEGO pieces feature a diverse design that allows for the creation of structural designs with a high degree of freedom in movement, such as cars and cranes, as well as arms suitable for different types of robotics or to create a scaled model of a production line.
These robots can run software that is programmed similarly to Scratch, which operates on the “Smart Brick.” This brick can read data from the sensors and perform actions based on the input data. This facilitates the teaching of concepts related to robotics, engineering, and programming.
How project was developed?
The Smart Bricks of LEGO EV3 run their own OS, which executes programs developed with the LEGO EV3 software. This language has some limitations, making it challenging to create sophisticated software, such as the A* algorithm. Fortunately, there is a way to run an “embedded OS” called leJOS EV3, which allows Java code to be executed on the Smart Brick.
This OS enables the creation of a Java project with an A* implementation to solve the 8-puzzle. The code is publicly available in the GitHub repository “RobotLegoEV3Java8Puzzle,” where the building instructions for the robot’s structure can also be found.
Example of Project Running
In this video, the A* algorithm and the 8-puzzle are explained in Spanish, and the execution of the algorithm on the robot is shown.